数据结构与算法
coderljw 2024-10-13 大约 5 分钟
# 1. 中点
mid = L + ((R - L) >> 1)
# 2. 异或运算 ^
无进位相加,
0 ^ N等于 N,N ^ N等于 0,满足交换律与结合律。0 ^ 7 // => 7 7 ^ 7 // => 0 // 两数交换 let a = 3 let b = 4 a ^= b b ^= a a ^= b1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10- 数列中只有一个数出现奇数次,其余数出现偶数次,求出现奇数次的数?
const ary = [1, 2, 1, 7, 7, 1, 2, 1, 7] let num = 0 ary.map(i => (num ^= i)) console.log(num)1
2
3
4
5- 数列中有两个数出现奇数次,其余数出现偶数次,求出现奇数次的数?
num & (~num + 1)提取不为零数中最右侧的 1。const ary = [1, 2, 1, 7, 7, 1, 2, 1, 7, 9] let num1 = 0, // num1 = a ^ b,因为 a !== b,所以 num1 !== 0,num1 必然有一位为 1 num2 = 0 // num2 = a or b ary.map(i => (num1 ^= i)) let rightOne = num1 & (~num1 + 1) // 取出最右侧的 1 ary.map(i => i & rightOne && (num2 ^= i)) // 划分 a、b,将 a 或 b 赋值给 num2 console.log(num2, num1 ^ num2) // 两数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 3. master 公式
作用:剖析递归行为时间复杂度。
- log(b, a) > d 复杂度为
- log(b, a) = d 复杂度为
- log(b, a) < d 复杂度为
# 4.斐波那契数列
- 递归
function fibonacci(n) { return n < 3 ? 1 : fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2) }1
2
3- 尾调用优化递归
'use strict' function fibonacci(n, a = 1, b = 1) { return n < 3 ? b : fibonacci(n - 1, b, a + b) }1
2
3
4- 循环
function fibonacci(n) { if (n < 3) return 1 let ary = [1, 1] let i = n + 1 - 2 while (i > 1) { const [a, b] = [ary[ary.length - 2], ary[ary.length - 1]] ary.push(a + b) i-- } return ary.at(-1) // ary.slice(-1)[0] }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 5. 排序算法
1.1 传统冒泡排序
function bubbleSort(ary) { const len = ary.length for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++) { // 相邻元素两两对比 if (ary[j] > ary[j + 1]) { ;[ary[j], ary[j + 1]] = [ary[j + 1], ary[j]] } } } return ary }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
141.2 改进冒泡排序
设置一标志性变量 pos,用于记录每趟排序中最后一次进行交换的位置。由于 pos 位置之后的记录均已交换到位,故在进行下一趟排序时只要扫描到 pos 位置即可。
function bubbleSort(ary) { let i = ary.length - 1 // 初始时,最后位置保持不变 while (i > 0) { let pos = 0 // 每趟开始时,无记录交换 for (let j = 0; j < i; j++) if (ary[j] > ary[j + 1]) { pos = j // 记录交换的位置 ;[ary[j], ary[j + 1]] = [ary[j + 1], ary[j]] } i = pos // 记录下趟排序截止位置 } return ary }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13- 选择排序
function selectionSort(ary) { let len = ary.length let minIndex for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) { minIndex = i for (let j = i + 1; j < len; j++) { // 寻找最小的数,将最小数的索引保存 if (ary[j] < ary[minIndex]) minIndex = j } ;[ary[i], ary[minIndex]] = [ary[minIndex], ary[i]] } return ary }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
133.1 传统插入排序
function insertionSort(ary) { for (let i = 1; i < ary.length; i++) { const key = ary[i] let j = i - 1 // 依次与已排序数组比较 while (j >= 0 && ary[j] > key) { ary[j + 1] = ary[j] j-- } ary[j + 1] = key } return ary }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
133.2 改进插入排序
查找插入位置时使用二分查找的方式
function insertionSort(ary) { for (let i = 1; i < ary.length; i++) { const key = ary[i] // 二分法查找 let L = 0, R = i - 1 while (L <= R) { let mid = L + ((R - L) >> 1) if (key < ary[mid]) R = mid - 1 else L = mid + 1 } for (let j = i - 1; j >= L; j--) ary[j + 1] = ary[j] ary[L] = key } return ary }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17- 希尔排序
function shellSort(ary) { const len = ary.length let temp = 1 let gap = 1 // 动态定义间隔序列 while (gap < len / 5) gap = gap * 5 + 1 for (gap; gap > 0; gap = Math.floor(gap / 5)) { // 插入排序 for (let i = gap; i < len; i++) { temp = ary[i] let j = i - gap for (; j >= 0 && ary[j] > temp; j -= gap) { ary[j + gap] = ary[j] } ary[j + gap] = temp } } return ary }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20- 归并排序
function mergeSort(ary) { // 采用自上而下的递归方法 const len = ary.length if (len < 2) return ary const mid = len >> 1, left = ary.slice(0, mid), right = ary.slice(mid) return merge(mergeSort(left), mergeSort(right)) } function merge(left, right) { const res = [] while (left.length && right.length) { if (left[0] <= right[0]) res.push(left.shift()) else res.push(right.shift()) } while (left.length) res.push(left.shift()) while (right.length) res.push(right.shift()) return res }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20- 快速排序
function quickSort(ary) { const len = ary.length if (len < 2) return ary // 找基准,并把基准从原数组删除保存在变量pivot const pivotIndex = len >> 1 const pivot = ary.splice(pivotIndex, 1)[0] // 定义左右数组 const left = [], right = [] // 比基准小的放在left,比基准大的放在right for (let i = 0; i < ary.length; i++) { if (ary[i] <= pivot) left.push(ary[i]) else right.push(ary[i]) } // 拼接数组并分别递归 return quickSort(left).concat([pivot], quickSort(right)) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17- 堆排序
function heapSort(ary) { // 建堆 let heapSize = ary.length for (let i = (heapSize >> 1) - 1; i >= 0; i--) { heapify(ary, i, heapSize) } // 排序 for (let j = heapSize - 1; j >= 1; j--) { ;[ary[0], ary[j]] = [ary[j], ary[0]] heapify(ary, 0, --heapSize) } return ary } function heapify(ary, x, len) { const L = 2 * x + 1 const R = 2 * x + 2 let largest = x if (L < len && ary[L] > ary[largest]) largest = L if (R < len && ary[R] > ary[largest]) largest = R if (largest !== x) { ;[ary[x], ary[largest]] = [ary[largest], ary[x]] heapify(ary, largest, len) } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
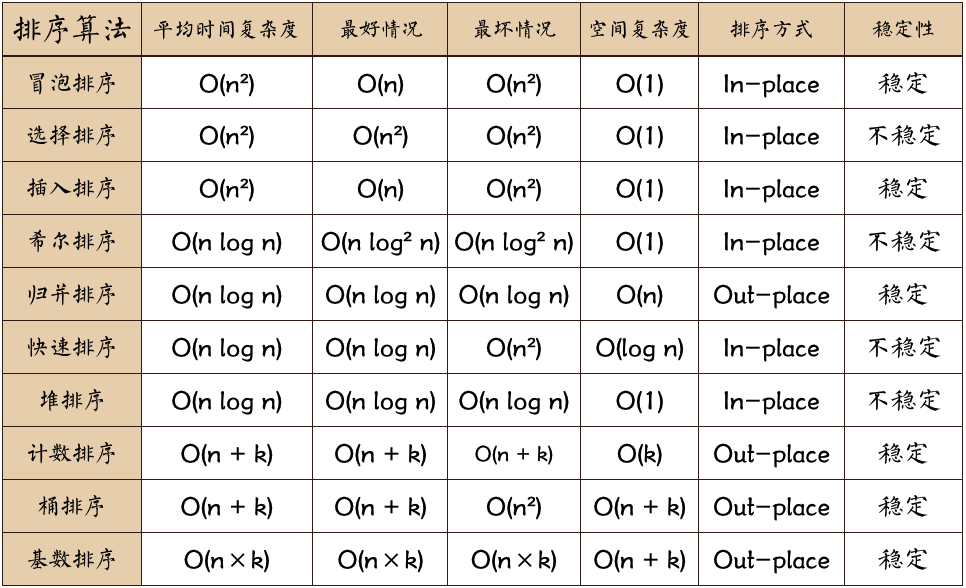
25十大经典排序算法总结 - Damonare (opens new window)
# 6. 二分法查找
function binarySearch(ary, target) {
let L = 0
let R = ary.length
while (L <= R) {
let mid = L + ((R - L) >> 1)
if (target === ary[mid]) return mid
else if (target < ary[mid]) R = mid - 1
else L = mid + 1
}
return -1
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 7. 树形数据结构化
const ary = [
{
id: 1,
pid: 0,
title: 'jack',
},
{
id: 2,
pid: 0,
title: 'pony',
},
{
id: 3,
pid: 1,
title: 'Evan You',
},
{
id: 4,
pid: 3,
title: 'coderljw',
},
]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
- 递归
function formatDataTree(ary) {
const parents = ary.filter(p => p.pid === 0)
const children = ary.filter(c => c.pid !== 0)
aryToTree(parents, children)
return parents
function aryToTree(parents, children) {
parents.map(p => {
children.forEach((c, i) => {
if (p.id === c.pid) {
if (p.children) p.children.push(c)
else p.children = [c]
aryToTree(p.children, children)
}
})
})
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
- 扁平化处理
const tree = ary.filter(p => {
const children = ary.filter(c => p.id === c.pid)
children.length && (p.children = children)
return p.pid === 0
})
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5

