面试
coderljw 2024-10-13 大约 4 分钟
# 1. 执行上下文
var name = 'Smith' // 函数参数作用域或内部作用域有 name 声明,不会查找此处作用域上的 name
;(function (name) {
console.log(name) // => 输出 [Function name],函数声明优先级高于 var 声明,函数内部的 var name 声明会被忽略
var name = 'Neo' // var name 声明被忽略,name = 'Neo' 执行
function name() {} // 声明提升
console.log(name) // => 'Neo'
})('Trinity')
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 2. 运算符优先级
var a = { n: 1 }
var b = a
b.x = a = { n: 2 }
console.log(a.x) // => undefined
console.log(b.x) // => { n: 2 }
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
# 3. this
var value = 1
var foo = {
value: 2,
bar() {
return this.value
},
}
// this 为 foo
console.log(foo.bar()) // => 2
// (foo.bar) 不会进行计算,this 为 foo
console.log((foo.bar)()) // => 2
// 以下使用了 GetValue,this 在严格模式为 undefined,在非严格模式隐式转为全局对象(可以理解为在全局执行 bar())
console.log((foo.bar = foo.bar)()) // => 1
console.log((false || foo.bar)()) // => 1
console.log((foo.bar, foo.bar)()) // => 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 4. 具名自执行函数
;(function foo() {
console.log(foo) // => [Function foo]
foo = 777
console.log(window.foo) // => undefined
console.log(foo) // => [Function foo]
})()
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
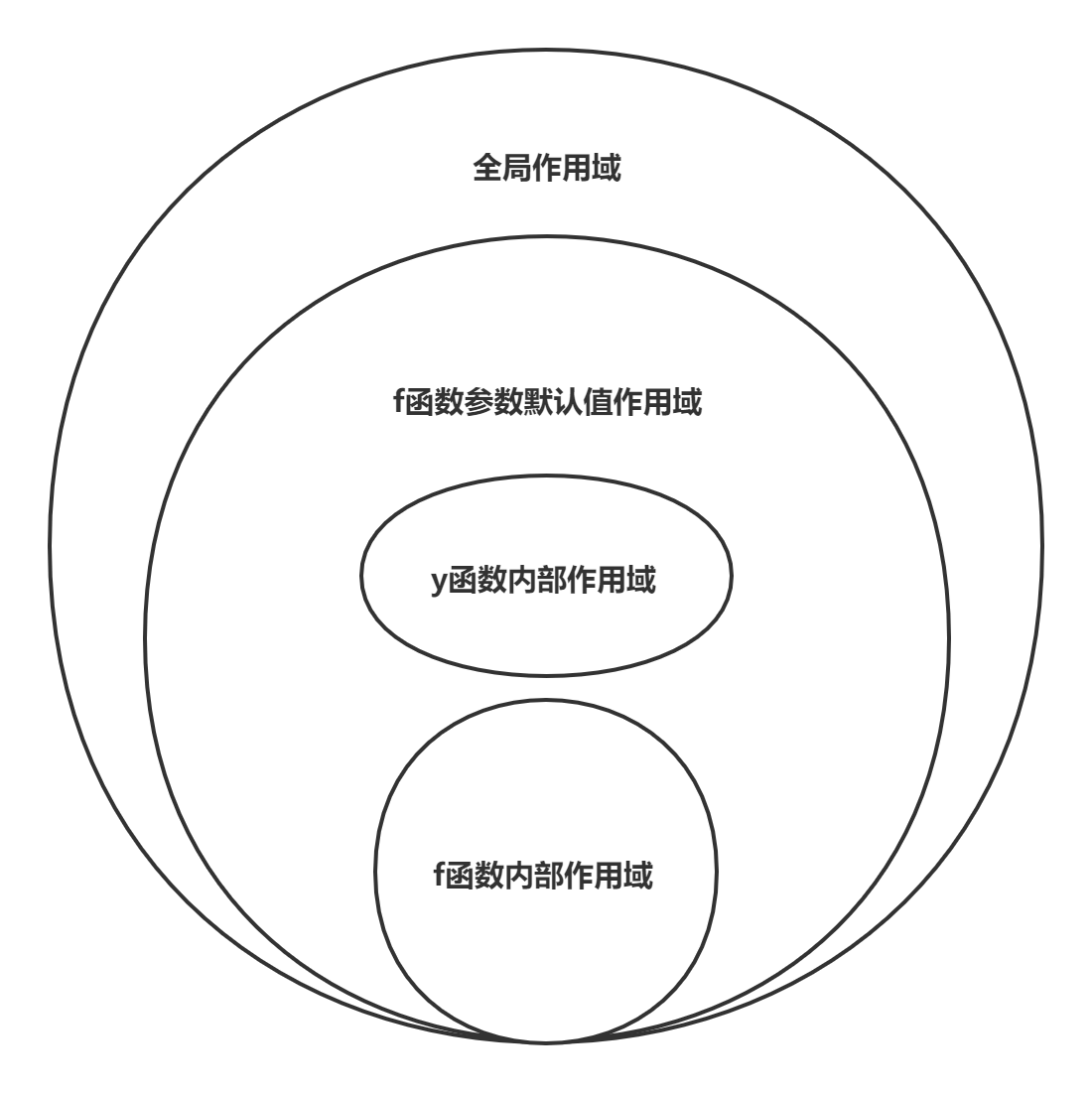
# 5. 作用域
var x = 1
function f(x, y = function () { x = 3; console.log(x); }) {
console.log(x)
var x = 2
y()
console.log(x)
}
f()
console.log(x)
// 依次打印:undefined -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
提示
# 6. 原型链
function Foo() {
getName = function () {
console.log(1)
}
return this
}
Foo.getName = function () {
console.log(2)
}
Foo.prototype.getName = function () {
console.log(3)
}
var getName = function () {
console.log(4)
}
function getName() {
console.log(5)
}
Foo.getName() // => 2
getName() // => 4
Foo().getName() // => 1
getName() // => 1
new Foo.getName() // => 2
new Foo().getName() // => 3
new new Foo().getName() // => 3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# 7. 事件循环(Event Loop)
如果 async2 返回的不是 promise,await 后续代码会直接注册到微任务队列中。
async function async1() { console.log('async1 start') await async2() console.log('async1 end') } async function async2() { console.log('async2') } console.log('script start') setTimeout(function () { console.log('setTimeout') }) async1() new Promise(function (resolve) { console.log('promise1') resolve() }).then(() => { console.log('promise2') }) console.log('script end') /* 依次打印:'script start' -> 'async1 start' -> 'async2' -> 'promise1' -> 'script end' -> 'async1 end' -> 'promise2' -> 'setTimeout' */1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31如果 async2 返回的是 promise,await 后续代码不会直接注册到微任务队列中。
async function async1() { console.log('async1 start') await async2() console.log('async1 end') } async function async2() { console.log('async2') return Promise.resolve().then(() => { console.log('async2 return end') }) } console.log('script start') setTimeout(function () { console.log('setTimeout') }) async1() new Promise(function (resolve) { console.log('promise1') resolve() }).then(() => { console.log('promise2') }) console.log('script end') /* 依次打印:'script start' -> 'async1 start' -> 'async2' -> 'promise1' -> 'script end' -> 'async2 return end' -> 'promise2' -> 'async1 end' -> 'setTimeout' */1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34async1、async2 相当于如下代码
async function async1() { console.log('async1 start') async2() .then(res => { console.log(res) }) .then(() => { console.log('async1 end') }) } async function async2() { console.log('async2') return 'async2 return end' }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15then() 参数非函数时发生值穿透(非异步)。
var date = new Date() console.log(1, new Date() - date) setTimeout(() => { console.log(2, new Date() - date) }, 500) Promise.resolve().then(console.log(3, new Date() - date)) // 阻塞线程 while (new Date() - date < 1000) {} console.log(4, new Date() - date) // 依次打印:1 0 -> 3 0 -> 4 1000 -> 2 10001
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 8. DFS & BFS
class Node {
constructor(val, left = null, right = null) {
this.val = val
this.left = left
this.right = right
}
}
const root = new Node(
1,
new Node(2, new Node(4), new Node(5)),
new Node(3, new Node(6))
)
console.log(root)
// 递归
function dfs(root) {
if (!root) return
console.log(root.val)
dfs(root.left)
dfs(root.right)
}
console.log('-------dfs--------')
dfs(root)
// 非递归
function dfs(root) {
if (!root) return
const queue = [root]
while (queue.length) {
const cur = queue.pop()
console.log(cur.val)
if (cur.right) queue.push(cur.right)
if (cur.left) queue.push(cur.left)
}
}
console.log('-------dfs--------')
dfs(root)
function bfs(root) {
if (!root) return
const queue = [root]
while (queue.length) {
const len = queue.length
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const cur = queue.shift()
console.log(cur.val)
if (cur.left) queue.push(cur.left)
if (cur.right) queue.push(cur.right)
}
}
}
console.log('-------bfs--------')
bfs(root)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
# 9. 控制请求并发数量
const fetch = (url, time) =>
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(url), time))
const task = [
() => fetch('api-1', 2000),
() => fetch('api-2', 1000),
() => fetch('api-3', 1000),
() => fetch('api-4', 2000),
() => fetch('api-5', 2000),
() => fetch('api-6', 1000),
]
const fetchLimit = async () => {
const limit = pLimit(2)
const promises = task.map(t => limit(t))
console.time('p-limit')
const res = await Promise.all(promises)
console.log(res)
console.timeEnd('p-limit')
}
const pLimit = concurrency => {
const queue = []
let activeCount = 0
const run = async (fn, resolve, args) => {
activeCount++
const result = await fn(...args)
resolve(result)
activeCount--
if (queue.length) queue.shift()()
}
const enqueue = (fn, resolve, args) => {
queue.push(run.bind(null, fn, resolve, args))
// 确保activeCount是最新值
;(async () => {
await Promise.resolve()
if (activeCount < concurrency && queue.length) queue.shift()()
})()
}
const generator = (fn, ...args) =>
new Promise(resolve => enqueue(fn, resolve, args))
return generator
}
fetchLimit()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
# 10. 连续触发时,若上一次 promise 执行未结束则直接废弃,只有最后一次 promise 会触发 then/reject
let count = 1
const promiseFunction = () =>
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(count++)))
const lastPromise = p => {
const cbs = []
return () =>
new Promise(resolve => {
cbs.push(resolve)
p().then(res => {
if (resolve === cbs.slice(-1)[0]) resolve(res)
})
})
}
const lastFn = lastPromise(promiseFunction)
lastFn().then(console.log) // 无输出
lastFn().then(console.log) // 无输出
lastFn().then(console.log) // 3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20

